Introduction

Children are among the most vulnerable members of society, requiring specialized care to support their growth, development, and overall health. Pediatric care focuses on providing comprehensive healthcare services tailored to the unique needs of infants, toddlers, adolescents, and young adults up to the age of 18. Hospitals play a critical role in ensuring that children receive timely and effective medical attention, ranging from preventive health checkups to treatment for acute and chronic diseases.
In recent years, advancements in medical technology, improvements in healthcare infrastructure, and increased awareness about children’s health have led to better treatment outcomes. However, challenges such as limited access to pediatric specialists, lack of awareness among parents, and the high cost of care still persist.
This article explores pediatric care in hospitals, highlighting its importance, the services offered, best practices, and ways in which families and healthcare providers can ensure safe and effective treatment for children.
Why Pediatric Care is Different from Adult Healthcare
Pediatric care goes beyond treating illnesses—it involves supporting every stage of a child’s physical, emotional, and mental development. Children are not just “small adults”; their bodies respond differently to medications, infections, and treatments.
Key Differences:
1. Developmental Considerations:
Pediatric doctors assess milestones such as speech, motor skills, and emotional development, which are essential to overall health.
2. Dosage and Treatment Adjustments:
Medicines and treatments must be carefully tailored based on weight, age, and organ maturity.
3. Communication:
Children may not articulate symptoms effectively. Pediatricians are trained to observe behavior and non-verbal cues.
4. Parental Involvement:
Treatment decisions often involve parents or guardians, requiring clear communication and counseling.
5. Focus on Prevention:
Pediatric care emphasizes immunization, nutrition, growth monitoring, and mental health alongside illness treatment.
Core Pediatric Services in Hospitals
Hospitals offering pediatric care are equipped with specialized facilities and medical professionals trained in child health. The following services form the backbone of pediatric care.
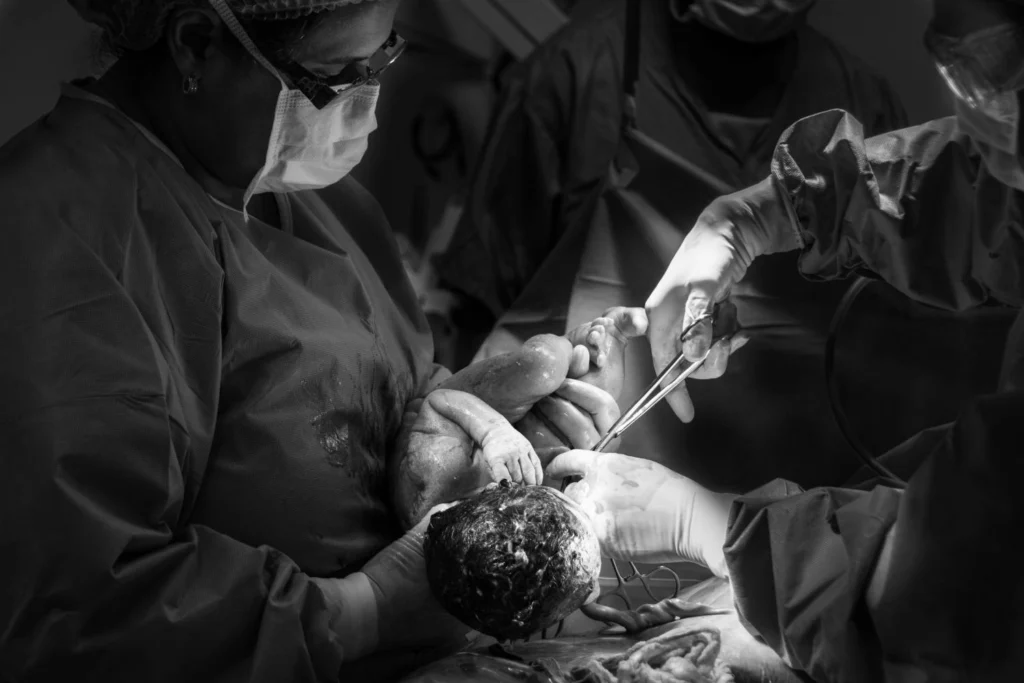
1. Neonatal and Infant Care

Specialized neonatal intensive care units (NICU) provide care for premature or critically ill newborns.
Monitoring breathing, feeding issues, infections, and congenital conditions.
Support for mothers with postnatal care and breastfeeding counseling.
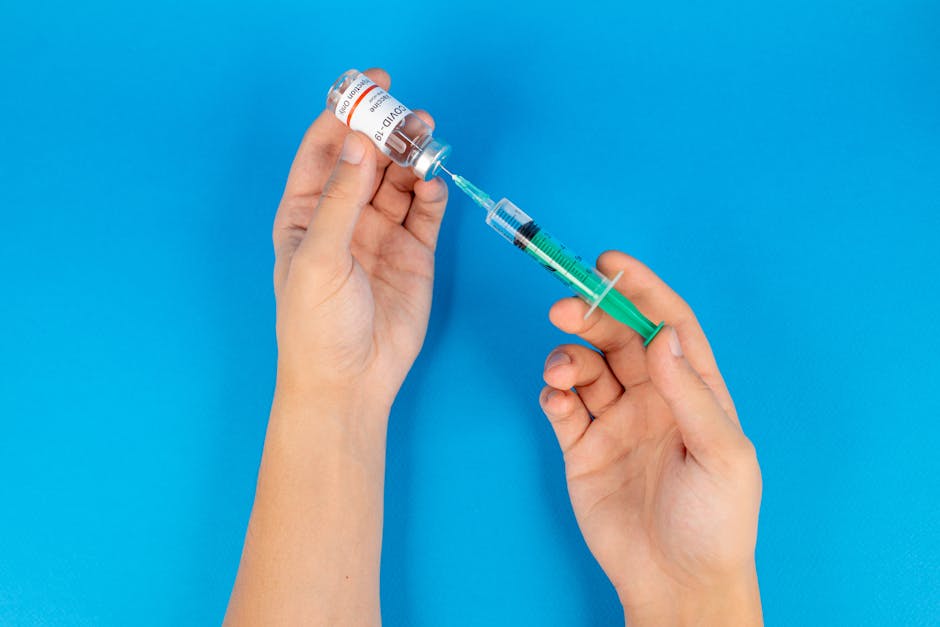
2. Immunization Programs
Scheduled vaccines protect against diseases like measles, mumps, polio, hepatitis, and more.
Pediatricians create customized vaccination plans and address concerns about vaccine safety.
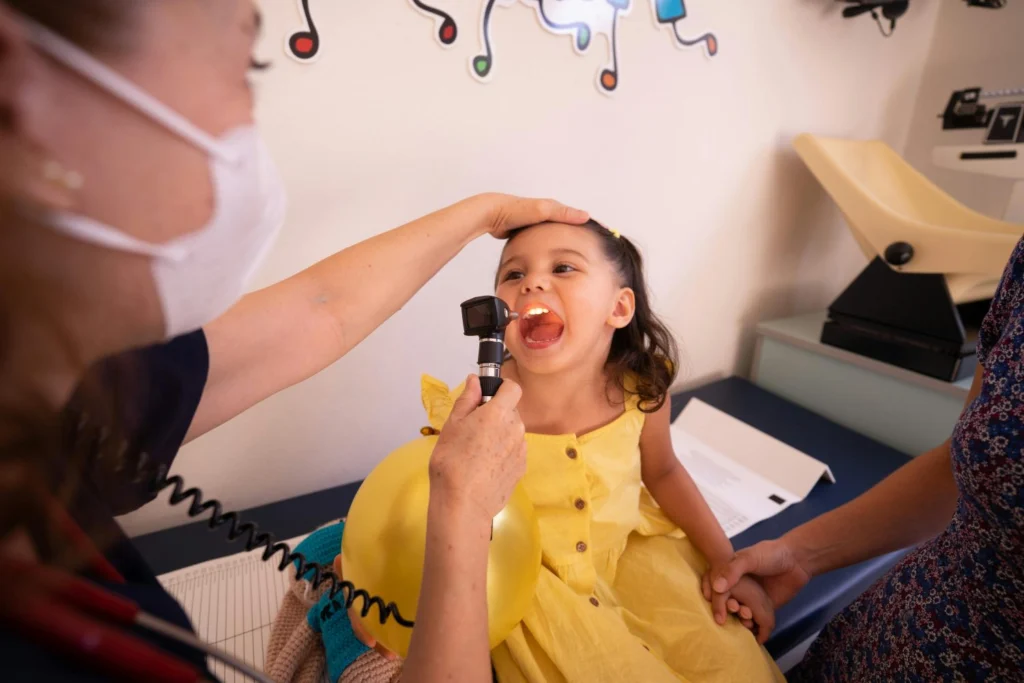
3. Pediatric Emergency Care

Handling urgent health conditions such as asthma attacks, allergic reactions, injuries, and dehydration.
Pediatric emergency teams are trained to stabilize young patients and refer them to specialists when required.
4. Chronic Disease Management

Support for children with conditions like diabetes, epilepsy, juvenile arthritis, or congenital heart defects.
Regular monitoring, therapy management, and long-term counseling.
5. Growth and Development Monitoring

Routine health checkups that track physical growth, developmental milestones, and behavioral patterns.
Early detection of learning disorders, speech delays, or developmental disorders.
6. Mental and Behavioral Health Support

Counseling for anxiety, depression, ADHD, or trauma.
Providing a supportive environment for children and parents to cope with emotional challenges.
7. Nutrition and Wellness

Diet plans tailored to a child’s age, activity level, and medical condition.
Guidance on weight management, eating habits, and preventing malnutrition.
Best Practices for Pediatric Care in Hospitals
To ensure safe and effective treatment, hospitals follow specific protocols and guidelines aligned with national and international standards.
1. Child-Friendly Infrastructure

Pediatric wards designed with colorful walls, toys, and entertainment systems to reduce anxiety.
Separate waiting areas to prevent exposure to infections from adult patients.
2. Trained Pediatric Specialists

Doctors, nurses, and technicians undergo specialized training in child health and behavior management.
Staff members are sensitive to communication barriers and empathetic care.
3. Infection Control Measures
Strict hygiene protocols in neonatal care units, operating rooms, and outpatient areas.
Use of sterilized instruments, isolation rooms, and personal protective equipment.
4. Family-Centered Care

Encouraging parental involvement in treatment decisions.
Providing counseling on medication management, home care, and post-treatment follow-up.
5. Safe Medication Administration
Accurate calculation of doses based on weight and age.
Monitoring for allergic reactions or side effects.
6. Ethical and Emotional Support
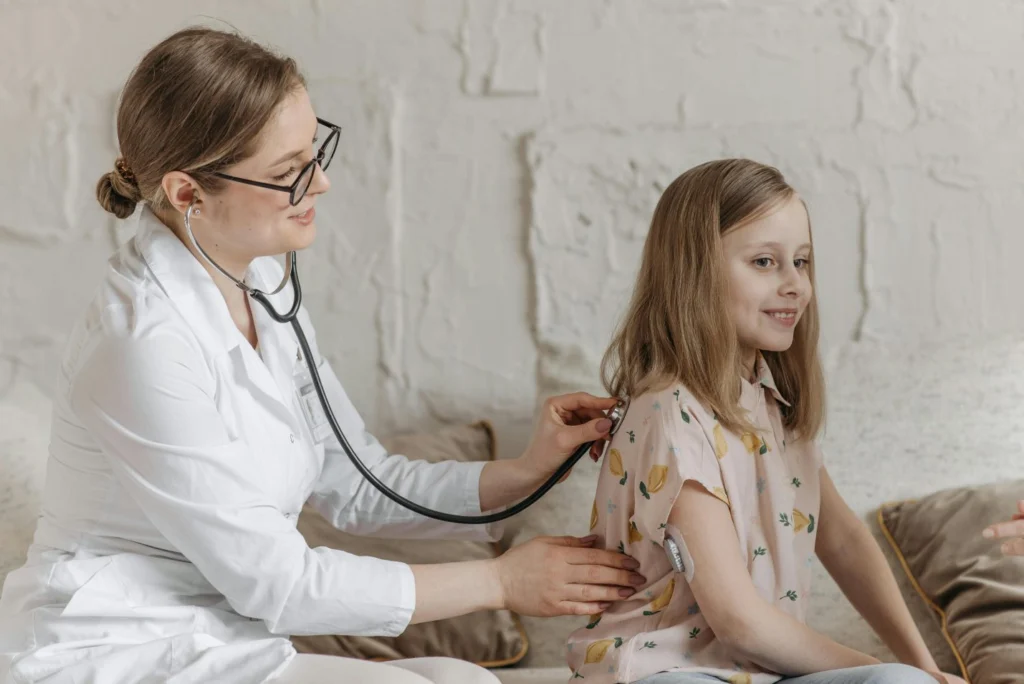
Pediatric care ensures that consent procedures are transparent and explained in age-appropriate language.
Emotional support teams assist families coping with long-term illnesses or terminal conditions.
Challenges in Pediatric Care
Despite significant improvements, several challenges hinder effective pediatric treatment in hospitals.
1. Shortage of Specialists
Many hospitals, especially in rural areas, face a lack of trained pediatricians and specialists.
2. High Treatment Costs
Advanced care, neonatal surgeries, and chronic disease management can be expensive, limiting access for lower-income families.
3. Parental Awareness
Some parents delay treatment due to misconceptions about symptoms or fear of hospital procedures.
4. Mental Health Stigma
Families are often hesitant to seek help for behavioral issues or psychological conditions.
5. Accessibility Issues
Transportation challenges and inadequate hospital infrastructure in remote areas prevent timely access to care.
Steps Families Can Take for Better Pediatric Care
Parents and guardians play an important role in ensuring their child’s health and safety. The following steps can help families navigate hospital care effectively.
1. Choose the Right Pediatric Facility
Research hospitals with certified pediatric units, trained doctors, and emergency care support.
2. Keep Health Records Updated
Maintain immunization charts, previous prescriptions, and medical history for faster diagnosis.
3. Communicate Openly
Share all symptoms, allergies, or behavioral changes with the pediatric team.
4. Understand Medications and Dosages
Follow prescriptions carefully and consult healthcare providers before giving new medications.
5. Stay Prepared for Emergencies
Keep a list of emergency contacts, vaccination schedules, and nearby pediatric hospitals.
6. Focus on Preventive Care
Regular checkups and timely vaccinations ensure long-term health benefits.
7. Seek Mental Health Support
Don’t hesitate to consult pediatric psychologists or counselors for emotional well-being.
The Role of Government and Private Institutions
Both government and private hospitals contribute to improving pediatric care through funding, awareness programs, and medical advancements.
Government Initiatives
•National immunization programs ensure vaccines reach remote areas.
•Subsidized healthcare schemes support underprivileged families.
•Training programs for healthcare providers enhance child-friendly care.
Private Sector Contributions
•Corporate partnerships fund child health research.
•Specialized pediatric hospitals offer state-of-the-art treatment options.
•Awareness campaigns on nutrition, hygiene, and mental health empower families.
Future Trends in Pediatric Healthcare
The pediatric care landscape is evolving with technological and medical innovations.
1. Telemedicine for Remote Consultations
Virtual consultations allow children in remote areas to access pediatric expertise without traveling long distances.
2. Personalized Medicine
Genetic profiling and targeted treatments offer customized care for children with rare diseases.
3. Mental Health Integration
Increasing awareness about emotional health is encouraging hospitals to integrate psychological counseling with medical care.
4. AI-Based Monitoring Tools
Wearable devices and smart health tracking systems help parents monitor vital signs and development milestones at home.
5. Community-Based Support Networks
Collaborations with schools and NGOs are creating awareness about early intervention and preventive care.
Conclusion
Pediatric care in hospitals is a vital aspect of building a healthier future for children. By offering specialized treatment, preventive care, and emotional support, healthcare providers ensure that children not only survive but thrive. Families, hospitals, and policymakers must work together to overcome challenges such as lack of access, awareness, and financial constraints.
With continued investment in healthcare infrastructure, training, and awareness programs, pediatric care can become safer, more effective, and more inclusive. Every child deserves the opportunity to grow, learn, and live a healthy life—and comprehensive pediatric care is the key to making that a reality.